来源:https://javaguide.cn/java/concurrent/virtual-thread.html
虚拟线程在 Java 21 正式发布,这是一项重量级的更新。
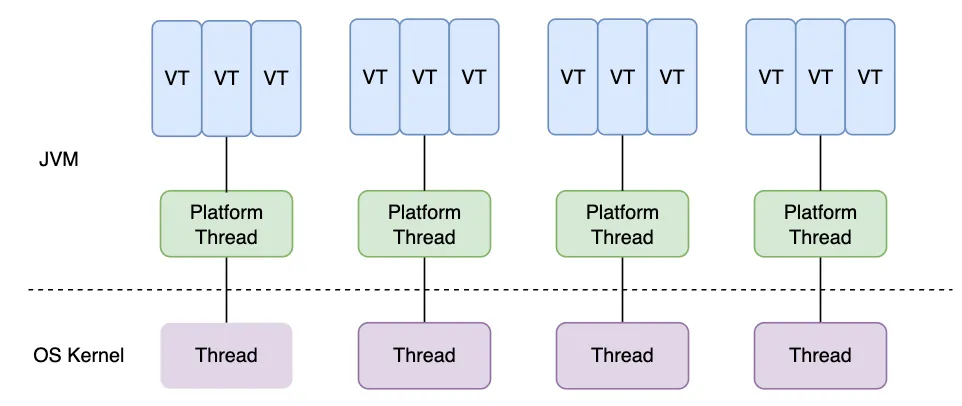
什么是虚拟线程? 虚拟线程(Virtual Thread)是 JDK 而不是 OS 实现的轻量级线程(Lightweight Process,LWP),由 JVM 调度。许多虚拟线程共享同一个操作系统线程,虚拟线程的数量可以远大于操作系统线程的数量。
虚拟线程和平台线程有什么关系? 在引入虚拟线程之前,java.lang.Thread包已经支持所谓的平台线程(Platform Thread),也就是没有虚拟线程之前,我们一直使用的线程。JVM 调度程序通过平台线程(载体线程)来管理虚拟线程,一个平台线程可以在不同的时间执行不同的虚拟线程(多个虚拟线程挂载在一个平台线程上),当虚拟线程被阻塞或等待时,平台线程可以切换到执行另一个虚拟线程。
虚拟线程、平台线程和系统内核线程的关系图如下所示(图源:How to Use Java 19 Virtual Threads ):
关于平台线程和系统内核线程的对应关系多提一点:在 Windows 和 Linux 等主流操作系统中,Java 线程采用的是一对一的线程模型,也就是一个平台线程对应一个系统内核线程。Solaris 系统是一个特例,HotSpot VM 在 Solaris 上支持多对多和一对一。具体可以参考 R 大的回答:JVM 中的线程模型是用户级的么?
虚拟线程优缺点 优点 非常轻量级 :可以在单个线程中创建成百上千个虚拟线程而不会导致过多的线程创建和上下文切换。简化异步编程 :虚拟线程可以简化异步编程,使代码更易于理解和维护。它可以将异步代码编写得更像同步代码,避免了回调地狱(Callback Hell)。减少资源开销 :由于虚拟线程是由 JVM 实现的,它能够更高效地利用底层资源,例如 CPU 和内存。虚拟线程的上下文切换比平台线程更轻量,因此能够更好地支持高并发场景。缺点 不适用于计算密集型任务 :虚拟线程适用于 I/O 密集型任务,但不适用于计算密集型任务,因为密集型计算始终需要 CPU 资源作为支持。与某些第三方库不兼容 :虽然虚拟线程设计时考虑了与现有代码的兼容性,但某些依赖平台线程特性的第三方库可能不完全兼容虚拟线程。如何创建虚拟线程 官方提供了以下四种方式创建虚拟线程:
使用 Thread.startVirtualThread() 创建 使用 Thread.ofVirtual() 创建 使用 ThreadFactory 创建 使用 Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor()创建 1)使用 Thread.startVirtualThread() 创建
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public class VirtualThreadTest {public static void main (String[] args) {CustomThread customThread = new CustomThread ();static class CustomThread implements Runnable {@Override public void run () {"CustomThread run" );
2)使用 Thread.ofVirtual() 创建
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public class VirtualThreadTest {public static void main (String[] args) {CustomThread customThread = new CustomThread ();Thread unStarted = Thread.ofVirtual().unstarted(customThread);static class CustomThread implements Runnable {@Override public void run () {"CustomThread run" );
3)使用 ThreadFactory 创建
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class VirtualThreadTest {public static void main (String[] args) {CustomThread customThread = new CustomThread ();ThreadFactory factory = Thread.ofVirtual().factory();Thread thread = factory.newThread(customThread);static class CustomThread implements Runnable {@Override public void run () {"CustomThread run" );
4)使用 Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor()创建
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public class VirtualThreadTest {public static void main (String[] args) {CustomThread customThread = new CustomThread ();ExecutorService executor = Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor();static class CustomThread implements Runnable {@Override public void run () {"CustomThread run" );
虚拟线程和平台线程性能对比 通过多线程和虚拟线程的方式处理相同的任务,对比创建的系统线程数和处理耗时。
说明: 统计创建的系统线程中部分为后台线程(比如 GC 线程),两种场景下都一样,所以并不影响对比。
测试代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 public class VirtualThreadTest {static List<Integer> list = new ArrayList <>();public static void main (String[] args) {ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1 );ThreadMXBean threadBean = ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean();false , false );10 , 10 , TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);long start = System.currentTimeMillis();ExecutorService executor = Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor();for (int i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i++) {try {500 );catch (InterruptedException ignored) {"max:" + list.get(0 ) + " platform thread/os thread" );"totalMillis:%dms\n" , System.currentTimeMillis() - start);private static void updateMaxThreadNum (int num) {if (list.isEmpty()) {else {Integer integer = list.get(0 );if (num > integer) {0 , num);
请求数 10000 单请求耗时 1s:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 22 platform thread/os thread209 platform thread/os thread509 platform thread/os thread1009 platform thread/os thread2009 platform thread/os thread
请求数 10000 单请求耗时 0.5s:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 22 platform thread/os thread209 platform thread/os thread509 platform thread/os thread1009 platform thread/os thread2009 platform thread/os thread
可以看到在密集 IO 的场景下,需要创建大量的平台线程异步处理才能达到虚拟线程的处理速度。 因此,在密集 IO 的场景,虚拟线程可以大幅提高线程的执行效率,减少线程资源的创建以及上下文切换。 注意:有段时间 JDK 一直致力于 Reactor 响应式编程来提高 Java 性能,但响应式编程难以理解、调试、使用,最终又回到了同步编程,最终虚拟线程诞生。
虚拟线程的底层原理 详见:虚拟线程 - VirtualThread源码透视 - throwable - 博客园